Cell Cycle Pie Chart
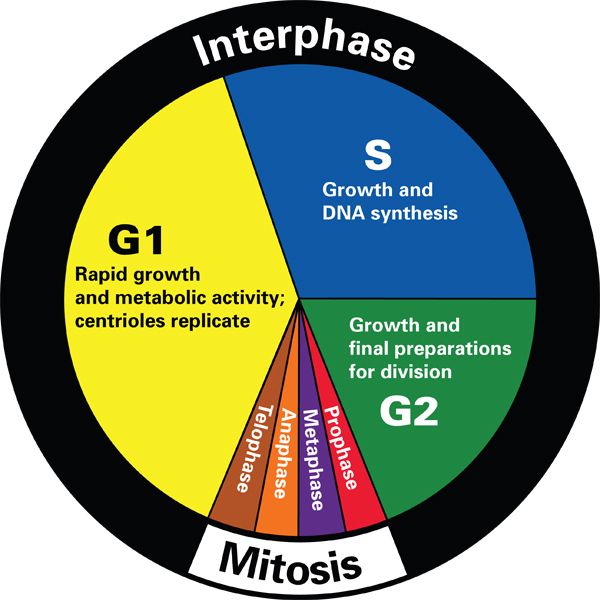
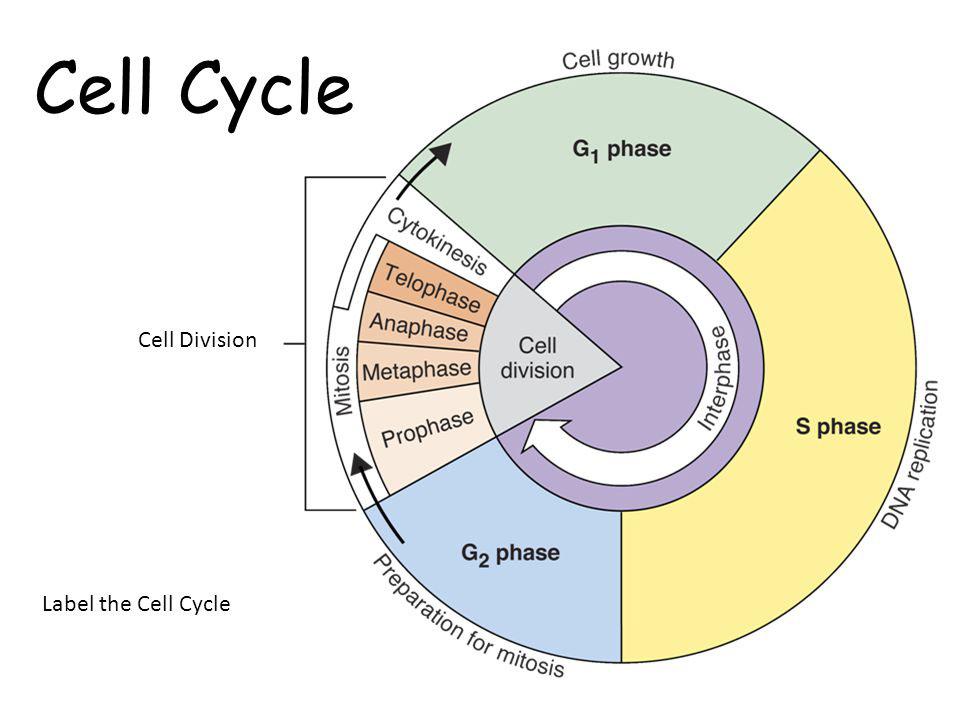
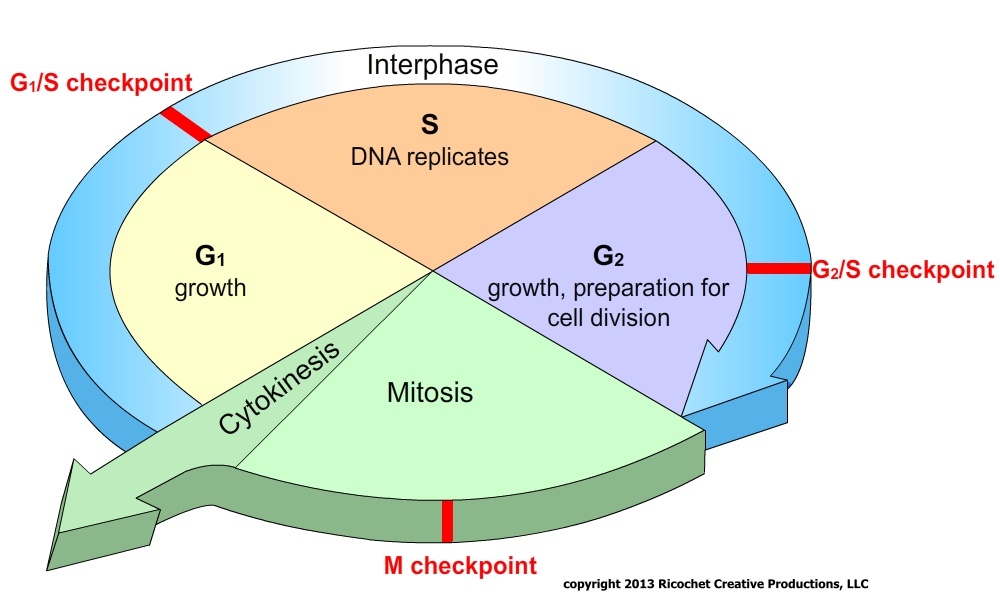
Cell Cycle Pie Chart - Review the stages of the cell cycle, including the checkpoints, and identify the key features of each stage. Web revise mitosis, the cell cycle and how stem cells work in humans and plants for gcse biology, aqa. Which phases of the cell cycle will have cells with twice the amount of dna? Web the cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. Interphase is divided into three phases: Finally, they split to produce two daughter cells. Gap 2 phase (g2) 5. The cell cycle has three phases: Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. Interphase is divided into three phases: Web measuring the cell cycle can include probing many aspects: It all starts with the parent cell growing in size and then making a copy of its genetic material. Web the cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next. The area of each chart is proportional to the overall cell cycle duration. Web a single cell will divide and generate many progeny, diversifying in a controlled and timely manner ( mueller et al., 2015) to generate cells with very different functions than the parent, all with the same genome ( wilmut et al., 1997 ). Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Mitosis phase (m) read more: In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Web the cell cycle and its phases are one of the most central concepts within cell biology. It includes information about why cells divide, and the steps involved in nuclear division: Web measuring the cell cycle can include probing many aspects: In which phase of the eukaryotic. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. Gap 1 (g 1), synthesis (s), gap 2 (g 2), and. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Web the cell cycle is the repeating pattern of cell growth. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is composed of interphase (g₁, s, and g₂ phases), followed by the mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), and g₀ phase. Web a single cell will divide and generate many progeny, diversifying in a controlled and timely manner ( mueller et al., 2015) to generate. Gap 1 (g 1), synthesis (s), gap 2 (g 2), and. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna. Phases of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. What are. Web start studying cell cycle pie chart. Mitosis phase (m) read more: Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Web the cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. Web most of the cell cycle is the period during which the cell is not dividing, which is called interphase. Which cell cycle phase a cell is in, or whether it has progressed beyond a given point of interest, such as a checkpoint or the completion of dna replication; The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Whether or not a cell is cycling or whether it retains. Web the graphic below shows a visual representation of the cell cycle. Gap 1 phase (g1) 3. This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. Finally, they split to produce two daughter cells. Web the cell cycle is composed of interphase (g₁, s, and g₂ phases), followed by the mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), and. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Web revise mitosis, the cell cycle and how stem cells work in humans and plants for gcse biology, aqa. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. As mentioned, the cell goes through a series of events in a specific order to. Web these notes go with a powerpoint presentation on the cell cycle and mitosis. Interphase is followed by the mitotic phase. Interphase (g1, s and g2) nuclear division (mitosis) cell division (cytokinesis) the length of the cell cycle is very variable depending on environmental conditions, the cell type and the organism. Once you have it correct draw and label the. Web each pie chart shows the fraction of the cell cycle devoted to each of the primary stages of the cell cycle. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna. It includes information about why cells divide, and the steps involved in nuclear division: Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Cell cycle durations reflect minimal doubling times under ideal conditions. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components: In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Web most of the cell cycle is the period during which the cell is not dividing, which is called interphase. The area of each chart is proportional to the overall cell cycle duration. As mentioned, the cell goes through a series of events in a specific order to divide. Web start studying cell cycle pie chart. Web these notes go with a powerpoint presentation on the cell cycle and mitosis. Whether or not a cell is cycling or whether it retains the potential to cycle; Interphase is divided into three phases:cell cycle pie chart Diagram Quizlet
Teaching the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Cell Cycle Graph
The Cell Cycle in Eukaryotes College Board AP Biology Revision Notes
Phases of Cell cycle Online Biology Notes
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division
Cell Cycle Pie Chart
SOLVED Draw the Cell Cycle Diagram Basic pie chart with stages of
Cell cycle pie chart
Learn Vocabulary, Terms, And More With Flashcards, Games, And Other Study Tools.
Review The Stages Of The Cell Cycle, Including The Checkpoints, And Identify The Key Features Of Each Stage.
A Large Circle Is Drawn, With Sectors Of The Circle Identified To Correspond To Various Stages Of The Cell Cycle, Such As The G1 (Cell Growth), S (Synthesis) And G2 (Cell Growth) Stages.
This Cell Cycle Is Used By All Eukaryotic Cells To Produce New Cells.
Related Post: