Time Signature Chart
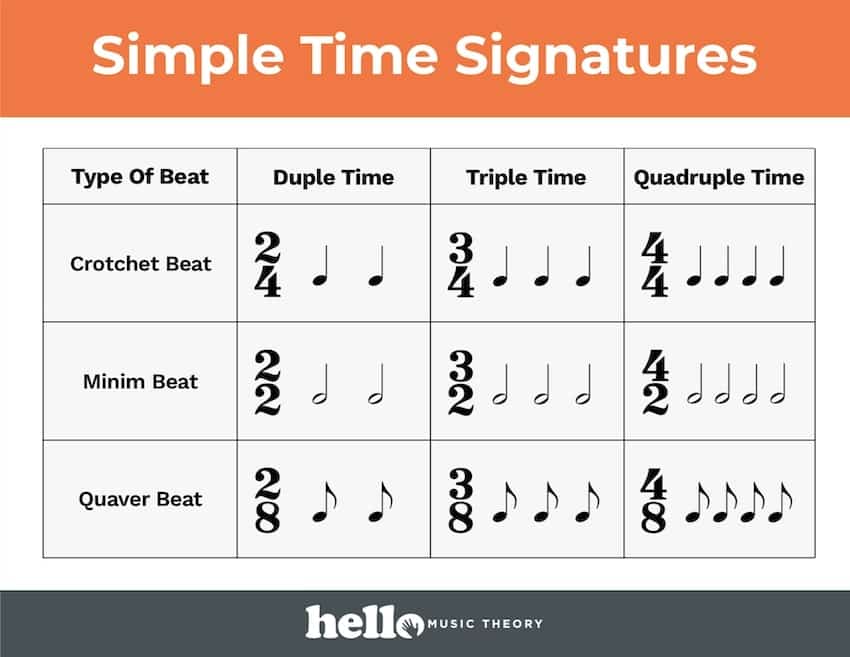
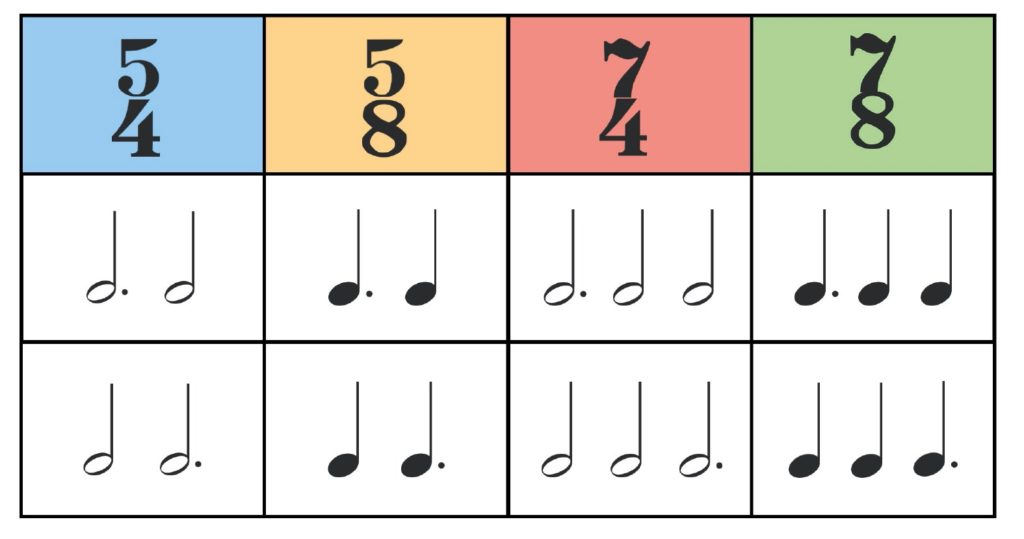
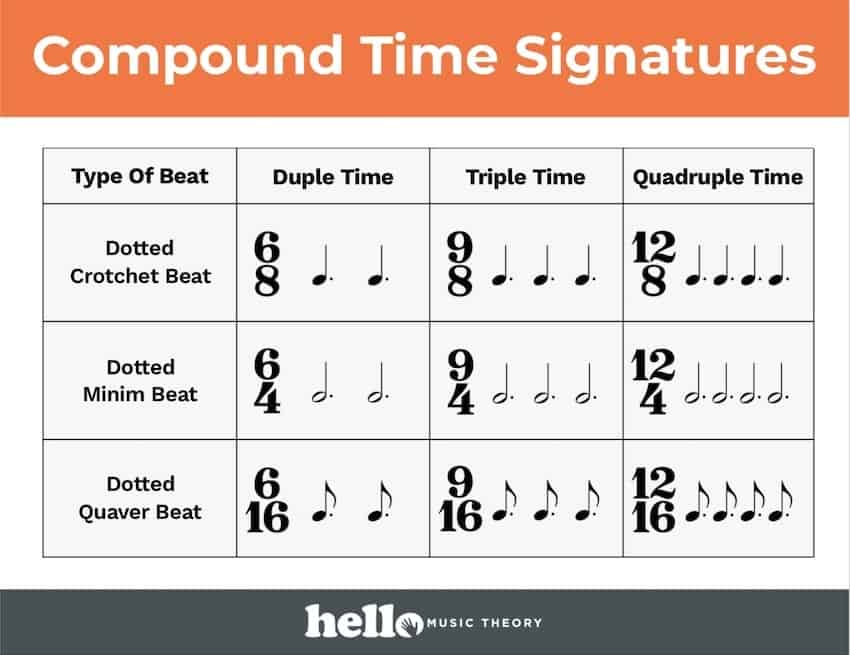
Time Signature Chart - When it comes to reading music, understanding time signatures is essential to understanding musical notation and the rhythm of a piece of sheet music. Web a time signature, also known as a time meter, is made up of two numbers, one on top of the other. It consists of two numbers on top of each other (a bit like a fraction in math, but without the line). Web a time signature appears at the beginning of a piece of music to show the time or meter of the music. All the time meters in these charts are regular time signatures. Web learn the basics of time signatures, how to read them, how they are categorized into meters, and why composers may choose some time signatures over others! With the help of time signatures and tempo. A regular time signature is one which represents 2, 3 or 4 main beats per bar. Here are some different time signatures you might see in a piece of music. It looks a bit like a fraction. When it comes to reading music, understanding time signatures is essential to understanding musical notation and the rhythm of a piece of sheet music. There are three main types of time signatures: Web a time signature, also known as a time meter, is made up of two numbers, one on top of the other. With the help of time signatures and tempo. A regular time signature is one which represents 2, 3 or 4 main beats per bar. Web in sheet music, the time signature appears at the beginning of a piece as a symbol or stacked numerals immediately following the key signature (or immediately following the clef symbol if the key signature is empty). Web time signatures tell us how many beats of music there are per measure and which musical note represents a single ‘beat’ in the particular song. We use time signatures to tell musicians how to group musical notes. Web guide to time signatures in music: Triple time means 3 main beats per bar. We use time signatures to tell musicians how to group musical notes. Web in this article, we’ll cover what time signatures in music are, why they’re used, how to interpret them, plus a few examples of common and uncommon time signatures in different genres. Web learn the basics of time signatures, how to read them, how they are categorized into. It consists of two numbers on top of each other (a bit like a fraction in math, but without the line). A regular time signature is one which represents 2, 3 or 4 main beats per bar. Web on this page, i’ve put together some time signature charts of different simple and compound time signatures and how we arrange them. Web this time signature chart shows the most common regular time signatures. Web guide to time signatures in music: Web in sheet music, the time signature appears at the beginning of a piece as a symbol or stacked numerals immediately following the key signature (or immediately following the clef symbol if the key signature is empty). All the time meters. A regular time signature is one which represents 2, 3 or 4 main beats per bar. All the time meters in these charts are regular time signatures. Web a time signature appears at the beginning of a piece of music to show the time or meter of the music. We use time signatures to tell musicians how to group musical. Duple time means 2 main beats per bar. Web in this article, we’ll cover what time signatures in music are, why they’re used, how to interpret them, plus a few examples of common and uncommon time signatures in different genres. There are three main types of time signatures: It consists of two numbers on top of each other (a bit. We use time signatures to tell musicians how to group musical notes. There are three main types of time signatures: Nov 2, 2021 • 3 min read. Web time signatures tell us how many beats of music there are per measure and which musical note represents a single ‘beat’ in the particular song. With the help of time signatures and. It consists of two numbers on top of each other (a bit like a fraction in math, but without the line). Web a time signature, also known as a time meter, is made up of two numbers, one on top of the other. It looks a bit like a fraction. Web time signatures tell us how many beats of music. Here are some different time signatures you might see in a piece of music. It consists of two numbers on top of each other (a bit like a fraction in math, but without the line). Web guide to time signatures in music: Web on this page, i’ve put together some time signature charts of different simple and compound time signatures. Here are some different time signatures you might see in a piece of music. Triple time means 3 main beats per bar. We use time signatures to tell musicians how to group musical notes. Web learn the basics of time signatures, how to read them, how they are categorized into meters, and why composers may choose some time signatures over. Web time signatures tell us how many beats of music there are per measure and which musical note represents a single ‘beat’ in the particular song. Web on this page, i’ve put together some time signature charts of different simple and compound time signatures and how we arrange them into duple, triple, and quadruple time. The top number shows the. All the time meters in these charts are regular time signatures. We use time signatures to tell musicians how to group musical notes. Web a time signature appears at the beginning of a piece of music to show the time or meter of the music. With the help of time signatures and tempo. Web time signatures tell us how many beats of music there are per measure and which musical note represents a single ‘beat’ in the particular song. Web a time signature, also known as a time meter, is made up of two numbers, one on top of the other. The top number shows the number of beats in every measure (bar). Web guide to time signatures in music: Triple time means 3 main beats per bar. Nov 2, 2021 • 3 min read. Duple time means 2 main beats per bar. Here are some different time signatures you might see in a piece of music. There are three main types of time signatures: Web in this article, we’ll cover what time signatures in music are, why they’re used, how to interpret them, plus a few examples of common and uncommon time signatures in different genres. Web in sheet music, the time signature appears at the beginning of a piece as a symbol or stacked numerals immediately following the key signature (or immediately following the clef symbol if the key signature is empty). Web on this page, i’ve put together some time signature charts of different simple and compound time signatures and how we arrange them into duple, triple, and quadruple time.Time Signature Charts Hello Music Theory
Reading rhythm, part 12 time signatures
Grade 5 Music Theory Time Signatures Jade Bultitude
Time Signature In Musical Notation Phamox Music
Time Signatures and Meter A Beginner's Guide Rebecca's Piano Keys
Time Signatures in Music Explained
Time Signature Charts Hello Music Theory
Time Signatures & Meters Everything you need to know School of
Time Signatures What are they and how do they work?
how to determine time signature
A Regular Time Signature Is One Which Represents 2, 3 Or 4 Main Beats Per Bar.
It Consists Of Two Numbers On Top Of Each Other (A Bit Like A Fraction In Math, But Without The Line).
Web Learn The Basics Of Time Signatures, How To Read Them, How They Are Categorized Into Meters, And Why Composers May Choose Some Time Signatures Over Others!
It Looks A Bit Like A Fraction.
Related Post: